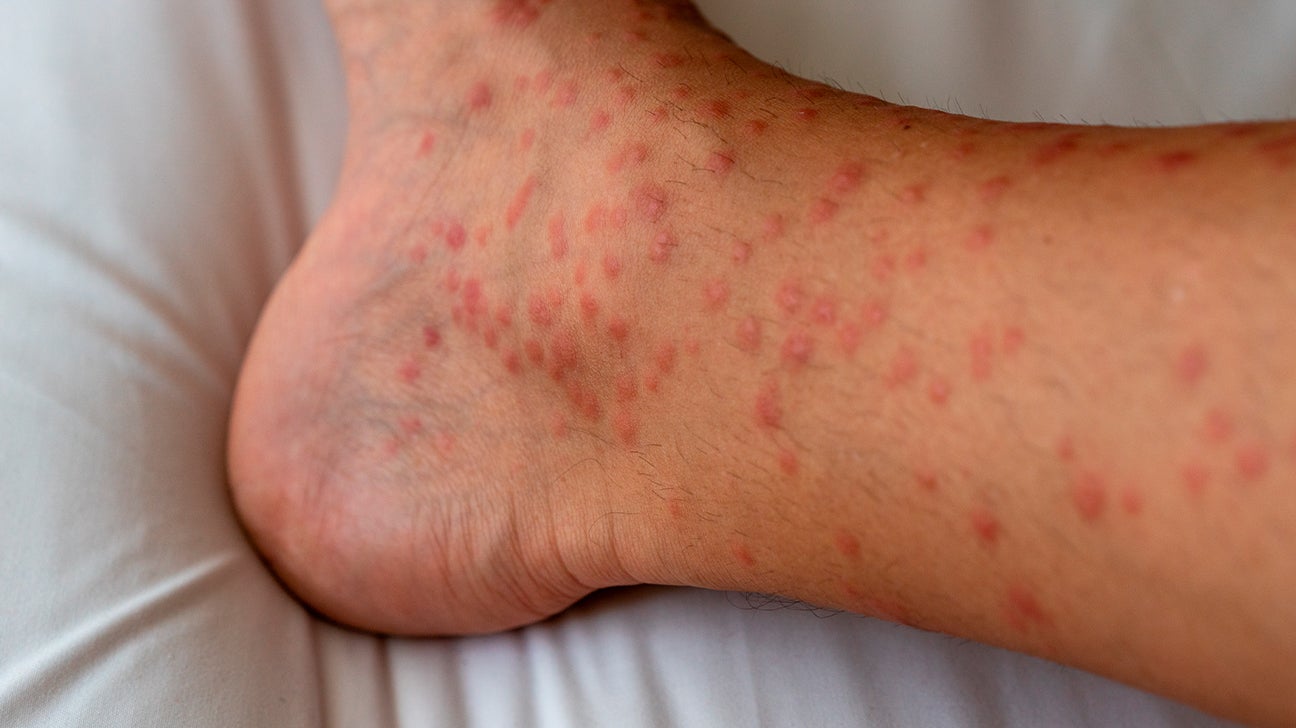
Rashes are areas of irritated or swollen skin on your body, often accompanied by pain and itching. Self-treating a rash inadvertently worsens the problem, so it is important to see Michael Rains M.D., FAAD, for diagnosis to establish the cause and receive the right treatment. Like most skin conditions, you either have a genetic predisposition to rashes. You may develop a rash due to one of the following skin conditions.
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a type of eczema that commonly affects young children but can occur at any age. It is the most common type of eczema, but people often use the two terms interchangeably. Symptoms of atopic dermatitis, including dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, can be confused with psoriasis, but they are different. Both conditions can cause red, raised, itchy skin patched on the hands and scalp. However, unlike psoriasis, eczema tends to come with intense itching. The causes are also different; psoriasis is an autoimmune disease, while eczema could result from genetic or environmental factors.
Eczema damages your skin barrier, making it susceptible to loss of moisture. As such, anything allergenic and irritating can enter your skin easily, making you susceptible to rashes and infections.
Drug rash
A rash may be a side effect of taking a certain medication or an allergic reaction to the drug. Diuretics or water pills, antibiotics, or many other medicines can cause a drug rash. Usually, a rash resulting from an allergic reaction or a side effect of a medication shows up within an hour of taking the new drug. Occasionally, it might take a few days to appear. The color of the spots varies from person to person, depending on one’s skin color. Usually, the rash clears up in days to weeks after you stop taking the medication. Although rare, a drug rash can be a part of anaphylaxis – a severe and potentially life-threatening reaction that affects breathing. Such cases require emergency care.
Hives
Hives, also known as urticarial, are a mysterious and sometimes random skin condition that may come and go. It has several triggers, including insect bites, extreme cold or heat, certain medications, and some foods such as nuts, eggs, and peanuts. Hives can also be linked to a genetic component whereby people are prone to asthma, allergy, and eczema. Your body responds to the trigger by releasing histamine –a chemical that causes your body to go into inflammatory overdrive to get rid of the allergen. Hives and swelling result as your body responds to histamine.
Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that mainly affects the face and is more common in women and light-skinned people. However, the symptoms of rosacea can be worse in men. Signature symptoms of this skin condition include redness across the forehead, nose, cheeks, and chin. These symptoms may occasionally flare up due to triggers such as cosmetics, exercise, hot drinks, spicy foods, emotional stress, alcoholic beverages, sunlight, and extreme temperatures. These triggers increase blood flow to the skin surface but vary from person to person.
There is no cure for rosacea, but there are effective treatments to help you control or minimize signs and symptoms. Identifying your potential triggers and avoiding them will also help you prevent flare-ups.
To learn more about skin conditions that cause rashes, consult your skin specialist at Beacon Dermatology.






